hankyoreh
Links to other country sites 다른 나라 사이트 링크
Auto plants being put to use for solar power production
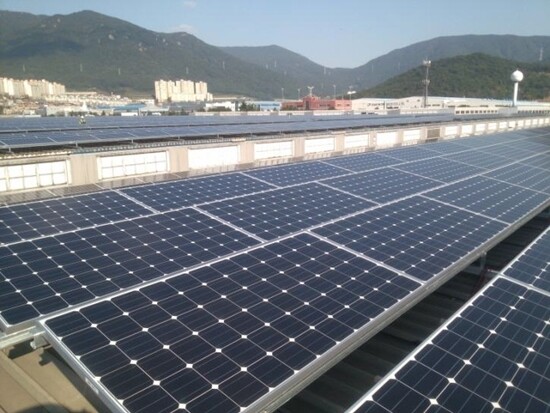

Large factory sites for domestic automobile assembly and production are being utilized for solar power generation.
A shift in Seoul’s renewable energy policy from subsidies to renewable portfolio standards (RPS) has prompted power companies to make use of the large lots available at car plants. The automakers, for their part, stand to gain by acquiring future emissions rights cheaper from the power companies.
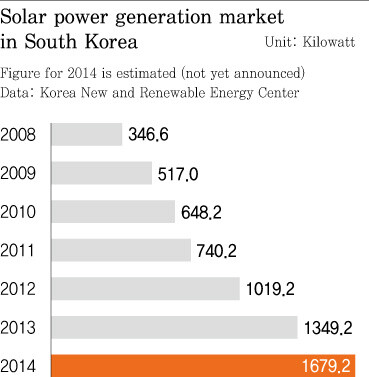
GM Korea began power production on Mar. 11 with a 11.5-megawatt solar power facility at its Changwon plant. The facility, which is capable of producing up to 14,000 megawatt-hours of electricity, was built with solar panels on the plant roof and parking area. Plant production and management are carried out by KC Cottrell in conjunction with Korea Southern Power and other partners, while GM Korea supplies the site.
Hyundai Motor is also producing power with a 10-MW roof-mounted solar power facility. Built in 2013, the solar module array consists of some 38,000 units covering 213,000 square meters of roof space at the company’s Asan plant. Renault Samsung is also operating a 20-MW solar power plant on the roof and a 300,000-㎡ loading site at its Busan plant. Asan production is being directed by Korea Midland Power, while Busan production is being led by Korea East-West Power, with output sold from both sites to the Korea Electric Power Corporation (KEPCO). Together, the three factories produce enough electricity to supply 4,000 to 8,000 nearby households.
The main reason for the use of automobile plant lots for solar power generation is a full-scale change in the administration’s new and renewable energy system. Large-scale power companies are now required to use new and renewable energies such as solar power to meet a certain percentage of their output - 3% in 2014. Those that fail to meet their RPS requirement are subject to penalties.
The government also supplies new and renewable energy credits to companies that meet with production and supply requirements. Power companies can buy and sell credits to meet their quotas.
Solar power is currently more expensive than ordinary electricity at market prices, resulting in a loss for automakers selling their output to KEPCO. But credit sales open an avenue to turning a profit. The government also extends more credits on a weighted basis when companies use factory roofs, loading sites, and other unused space to install solar panels.
By Cho Kye-wan, staff reporter
Please direct questions or comments to [english@hani.co.kr]

Editorial・opinion
![[Column] Park Geun-hye déjà vu in Yoon Suk-yeol [Column] Park Geun-hye déjà vu in Yoon Suk-yeol](https://flexible.img.hani.co.kr/flexible/normal/500/300/imgdb/original/2024/0424/651713945113788.jpg) [Column] Park Geun-hye déjà vu in Yoon Suk-yeol
[Column] Park Geun-hye déjà vu in Yoon Suk-yeol![[Editorial] New weight of N. Korea’s nuclear threats makes dialogue all the more urgent [Editorial] New weight of N. Korea’s nuclear threats makes dialogue all the more urgent](https://flexible.img.hani.co.kr/flexible/normal/500/300/imgdb/original/2024/0424/7317139454662664.jpg) [Editorial] New weight of N. Korea’s nuclear threats makes dialogue all the more urgent
[Editorial] New weight of N. Korea’s nuclear threats makes dialogue all the more urgent- [Guest essay] The real reason Korea’s new right wants to dub Rhee a founding father
- [Column] ‘Choson’: Is it time we start referring to N. Korea in its own terms?
- [Editorial] Japan’s rewriting of history with Korea has gone too far
- [Column] The president’s questionable capacity for dialogue
- [Column] Are chaebol firms just pizza pies for families to divvy up as they please?
- [Column] Has Korea, too, crossed the Rubicon on China?
- [Correspondent’s column] In Japan’s alliance with US, echoes of its past alliances with UK
- [Editorial] Does Yoon think the Korean public is wrong?
Most viewed articles
- 1[Column] Park Geun-hye déjà vu in Yoon Suk-yeol
- 2N. Korean hackers breached 10 defense contractors in South for months, police say
- 3Thursday to mark start of resignations by senior doctors amid standoff with government
- 4[Editorial] New weight of N. Korea’s nuclear threats makes dialogue all the more urgent
- 5Kim Jong-un expressed ‘satisfaction’ with nuclear counterstrike drill directed at South
- 6Will NewJeans end up collateral damage in internal feud at K-pop juggernaut Hybe?
- 7[Editorial] Japan’s rewriting of history with Korea has gone too far
- 8[Cine feature] A new shift in the Korean film investment and distribution market
- 9[Column] ‘Choson’: Is it time we start referring to N. Korea in its own terms?
- 10[Column] The clock is ticking for Korea’s first lady