hankyoreh
Links to other country sites 다른 나라 사이트 링크
Aging process of South Korean corporate sector prioritizes profitability over growth potential
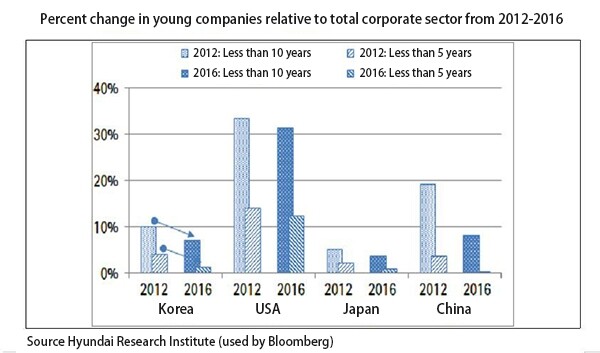
The percentage of publicly listed companies in South Korea that have existed for more than 10 years decreased 26% from four years ago, and growth indicators including sales and total assets have gotten much worse, a new report finds. The resulting diagnosis of the country’s corporate structure is that an aging process is underway in which companies seek stability by maintaining the status quo as they prioritize profitability while their growth potential declines.
According to a report titled “Current Status of Young Companies (10 Years and below) and Its Implications” that was published by the Hyundai Research Institute (HRI) on Apr. 10, there were 116 companies listed on stock exchanges (excluding financial companies) that had been established for 10 years or less (as of the end of 2016), which was down 26.6% from 2012. During this period, the total number of listed companies increased by 2.9%. As a consequence, the percentage of young companies fell from 10.1% in 2012 to 7.2%.
As for the fields which these young companies are located in, only 6% of them were in software and IT services, which represent the core of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. The field of materials accounted for 17% of these companies, while capital goods, durable goods and apparel, pharmaceuticals and bioengineering, and IT and hardware each took up 9%. The market capitalization of young companies as a percentage of total market capitalization slipped from 8.9% at the end of 2012 to 8.0% at the end of 2016. The rate of increase of market capitalization at young companies between 2012 and 2016 was 7.6%, which was much lower than the rate of increase of market capitalization at all the listed companies (19.2%).
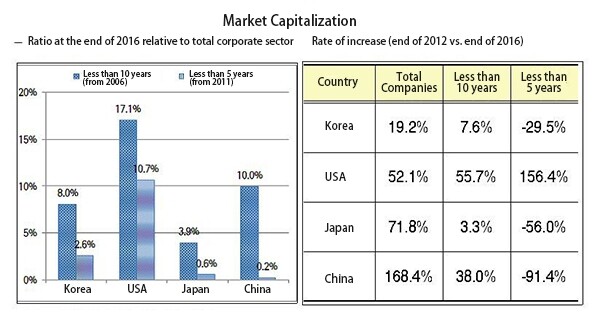
The report found that young companies’ growth indicators (sales and total assets) had taken a turn for the worse. Average sales across all listed companies during this time period fell by 16.6%, but young companies faced a drop of 34.7%. The average total assets per company across all listed companies increased by 2.9% while declining by 9.9% among young companies. They also had a low return on assets (ROA), a figure found by dividing net profits by total assets that shows corporate value. 54.9% of young companies had an ROA between 0-10% while 30.1% had a ratio below 0%, which shows that the majority of these companies have poor asset efficiency.
At the same time, young companies remained fairly profitable. As of the end of 2016, they had an operating margin of 6.9%, up 3.2 points from 2012. This was higher than the increase of 1.6 points in the operating margin for all listed companies during the same period. Young companies had a net profit ratio of 3.5%, which was lower than all listed companies (4.2%) but a 2-point improvement over 2012. The increase of the net profit ratio at young companies (0.7 points) was also higher than at all listed companies.
“This is an environment in which we could be seeing more start-ups whose business model is grounded in the industrial stimulus polices since the 2008 financial crisis and technology related to the Fourth Industrial Revolution and more ‘young companies’ created through the reorganization of existing companies. But despite this, the number of young companies in South Korea is actually decreasing. Since these younger companies tend to have less growth potential and to be only focused on profitability, the phenomenon of aging – of seeking safety by maintaining the status quo – appears to be affecting the corporate sector as well,” wrote Lee Jang-gyun, a senior analyst for HRI.
By Cho Kye-wan, staff reporter
Please direct questions or comments to [english@hani.co.kr]

Editorial・opinion
![[Column] Season 2 of special prosecutor probe may be coming to Korea soon [Column] Season 2 of special prosecutor probe may be coming to Korea soon](https://flexible.img.hani.co.kr/flexible/normal/500/300/imgdb/original/2024/0426/3317141030699447.jpg) [Column] Season 2 of special prosecutor probe may be coming to Korea soon
[Column] Season 2 of special prosecutor probe may be coming to Korea soon![[Column] Park Geun-hye déjà vu in Yoon Suk-yeol [Column] Park Geun-hye déjà vu in Yoon Suk-yeol](https://flexible.img.hani.co.kr/flexible/normal/500/300/imgdb/original/2024/0424/651713945113788.jpg) [Column] Park Geun-hye déjà vu in Yoon Suk-yeol
[Column] Park Geun-hye déjà vu in Yoon Suk-yeol- [Editorial] New weight of N. Korea’s nuclear threats makes dialogue all the more urgent
- [Guest essay] The real reason Korea’s new right wants to dub Rhee a founding father
- [Column] ‘Choson’: Is it time we start referring to N. Korea in its own terms?
- [Editorial] Japan’s rewriting of history with Korea has gone too far
- [Column] The president’s questionable capacity for dialogue
- [Column] Are chaebol firms just pizza pies for families to divvy up as they please?
- [Column] Has Korea, too, crossed the Rubicon on China?
- [Correspondent’s column] In Japan’s alliance with US, echoes of its past alliances with UK
Most viewed articles
- 1No good, very bad game for Korea puts it out of Olympics for first time since 1988
- 2[Column] Season 2 of special prosecutor probe may be coming to Korea soon
- 3Korea’s 1.3% growth in Q1 signals ‘textbook’ return to growth, says government
- 4‘We must say no’: Seoul defense chief on Korean, USFK involvement in hypothetical Taiwan crisis
- 5Is N. Korea threatening to test nukes in response to possible new US-led sanctions body?
- 6Division commander ordered troops to enter raging flood waters before Marine died, survivor says
- 7[Column] ‘Choson’: Is it time we start referring to N. Korea in its own terms?
- 8Will NewJeans end up collateral damage in internal feud at K-pop juggernaut Hybe?
- 9Korea sees more deaths than births for 52nd consecutive month in February
- 10[Editorial] Korea’s surprise Q1 growth requires objective assessment, not blind fanfare