hankyoreh
Links to other country sites 다른 나라 사이트 링크
For the elderly, medical cost burden getting heavier every year
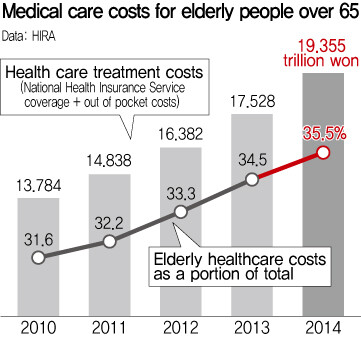
Medical costs for elderly South Koreans are skyrocketing every year. People over 65 account for 12% of the country‘s population, but spent 35% of all medical costs last year - a difference analysts attribute to the rapid aging trend and higher use of nursing home facilities than in the past.
A 2014 medical expense review published on Feb. 24 by the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service (HIRA) showed total health insurance costs totaling 54.53 trillion won (US$49.4 billion), an increase of 3.8 trillion won (US$3.4 billion), or 7.5%, from 2013. Treatment for people over 65 accounted for 19.35 trillion won (US$17.5 billion), registering the biggest increase at 10.4%. Per-patient costs for people over 70 totaled 3.62 million won (US$3,280), or more than three times the total average.
As part of the same trend, the percentage of total medical costs used by elderly people rose from 29.9% in 2010 to 35.5% last year.
The chief factor behind the increased costs last year was treatment for dementia and dental care. Dementia treatment costs for hospitalized seniors rose by 25% from the year before, the single largest increase, with a per-patient bill of 11.67 million won (US$10,570).
“The rate of increase has gone up because seniors with dementia who used to be cared for at home are now mostly being admitted to nursing homes,” explained Yoo Su-yeon, supervising researcher for HIRA.
Among outpatient seniors, the rate of treatment cost increase was highest for gingivitis and periodontal ailments (30.1%). Analysts attributed the rise to both an extension of health insurance coverage to false teeth, implants, scaling, and other dental services, and resulting increases in cavity and gum treatment.
The jump in medical costs is putting a stranglehold on the livelihood of poor elderly people. A questionnaire about the effectiveness of the basic pension system that the Ministry of Health and Welfare published in Dec. 2014 shows that elderly recipients of basic pension (up to 200,000 won a month) spend more money on health care (44.2%) than on food (30.2%) or lodging (15.8%).
Choi Hyo-suk, 74, who lives in Seoul’s Jongno District, said that she spent 150,000 won of her 200,000 won basic pension payment on visits to the doctor.
As medical costs for the elderly continue to mount each year, it is putting a burden on the fiscal health of the national health insurance system.
According to National Health Insurance Service figures made public by Rhee Mok-hee, a lawmaker with the New Politics Alliance for Democracy (NPAD) on the National Assembly Health and Welfare Committee, by 2020, the cost of elderly medical care will approach half (45.6%) of the total cost of medical care.
Experts say that the government needs to create a system of elderly health care management and focus on the prevention of chronic diseases. The most frequent causes of hospitalization for the elderly are cataracts and pneumonia, while the majority of elderly people receiving outpatient care have high blood pressure or acute bronchitis, confirming the importance of taking care of such chronic conditions.
“Hospitals provide different kinds of service, but elderly patients don’t take into account those differences when they visit the doctor. There needs to be an integrated care system that would help the elderly get treatment at the most appropriate institution,” said Seo Yeong-jun, a professor of health administration at Yonsei University.
“If a family doctor system were instituted for the elderly, it would help them monitor their health and prevent disease, which would ultimately reduce the cost of medical care,” Seo said.
By Park Su-ji, staff reporter
Please direct questions or comments to [english@hani.co.kr]

Editorial・opinion
![[Column] Park Geun-hye déjà vu in Yoon Suk-yeol [Column] Park Geun-hye déjà vu in Yoon Suk-yeol](https://flexible.img.hani.co.kr/flexible/normal/500/300/imgdb/original/2024/0424/651713945113788.jpg) [Column] Park Geun-hye déjà vu in Yoon Suk-yeol
[Column] Park Geun-hye déjà vu in Yoon Suk-yeol![[Editorial] New weight of N. Korea’s nuclear threats makes dialogue all the more urgent [Editorial] New weight of N. Korea’s nuclear threats makes dialogue all the more urgent](https://flexible.img.hani.co.kr/flexible/normal/500/300/imgdb/original/2024/0424/7317139454662664.jpg) [Editorial] New weight of N. Korea’s nuclear threats makes dialogue all the more urgent
[Editorial] New weight of N. Korea’s nuclear threats makes dialogue all the more urgent- [Guest essay] The real reason Korea’s new right wants to dub Rhee a founding father
- [Column] ‘Choson’: Is it time we start referring to N. Korea in its own terms?
- [Editorial] Japan’s rewriting of history with Korea has gone too far
- [Column] The president’s questionable capacity for dialogue
- [Column] Are chaebol firms just pizza pies for families to divvy up as they please?
- [Column] Has Korea, too, crossed the Rubicon on China?
- [Correspondent’s column] In Japan’s alliance with US, echoes of its past alliances with UK
- [Editorial] Does Yoon think the Korean public is wrong?
Most viewed articles
- 1[Column] Park Geun-hye déjà vu in Yoon Suk-yeol
- 2Will NewJeans end up collateral damage in internal feud at K-pop juggernaut Hybe?
- 3N. Korean hackers breached 10 defense contractors in South for months, police say
- 4[Guest essay] The real reason Korea’s new right wants to dub Rhee a founding father
- 5Up-and-coming Indonesian group StarBe spills what it learned during K-pop training in Seoul
- 6[Editorial] Japan’s rewriting of history with Korea has gone too far
- 7Why Korea shouldn’t welcome Japan’s newly beefed up defense cooperation with US
- 8Terry Anderson, AP reporter who informed world of massacre in Gwangju, dies at 76
- 9Thursday to mark start of resignations by senior doctors amid standoff with government
- 10Senior doctors cut hours, prepare to resign as government refuses to scrap medical reform plan