hankyoreh
Links to other country sites 다른 나라 사이트 링크
S. Korea’s local population to begin declining after peaking in 2020
According to government projections, South Korea’s local population will begin to decline after peaking this year. By 2040, the immigrant-derived population — including foreigners, naturalized citizens, and the children of immigrants — is expected to increase to 6.9% of the country’s total population.
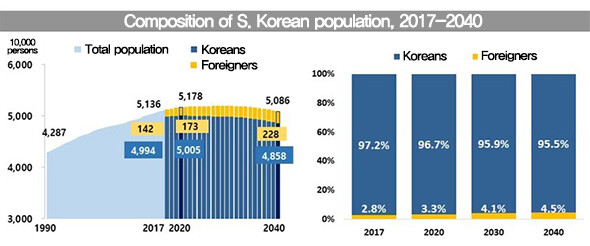
Statistics Korea, the government’s statistics office, released its 2019 long-term population projections on Oct. 15. According to the projections, Korea’s total population is projected to reach 51,781,000 people this year, consisting of 50,051,000 Korean citizens (96.7%) and 1,730,000 foreigners (3.3%).
The local population, which includes people born in the country, naturalized citizens, and the children of immigrants, will peak at 50.05 million this year and then enter a decline. Twenty years from now, in 2040, the population will decrease to 48.58 million. The local population will represent 95.5% of Korea’s total population (50,855,000), 1.2 points lower than this year. The foreign population will increase from 1.73 million this year to 2.28 million in 2040, representing 4.5% of the total population.
Though the local population has started to decline, an increasing number of foreigners will keep the total population from falling until 2028, when it tops out at 51.93 million.
The immigrant-derived population (defined to include current foreigners, naturalized as Korean citizens, and second-generation immigrants whose parents include at least one foreigner or naturalized Korean) is expected to increase from 2.22 million this year to 3.52 million in 2040, elevating its share of the total population from 4.3% to 6.9% over the same period. The statistics office attributes this to employment and marriage policies that the South Korean government has adopted since the mid-2000s to facilitate the influx of foreigners in response to the decline in the local population.
The local working-age population (15-64) will decrease by 8.77 million over the next 20 years, from 35.79 million this year to 27.03 million in 2040. That’s a huge drop as a share of the total population, from 55.6% to 71.5%. The working-age population will fall by about 360,000 people a year in the 2020s, as the baby boomers (born 1955-1963) enter old age, and then fall even faster, by 520,000 a year, in the 2030s.
The population aged 15-24 is slated to fall by 2.49 million (44%), from 5.64 million this year to 3.15 million in 2040, as its share of the local working-age population drops 4 points from 15.7% to 11.7%. While the middle-aged (50-64) population will shrink by 1.68 million (14%), from 12.06 million this year to 10.38 million in 2020, its share of the local working-age population will rise by 4.7 points, from 33.7% to 38.4%.
The local elderly population (aged 65 and above) is projected to increase from 8.03 million this year to more than 10 million (10.33 million) in 2025, five years later, and then to above 15 million in 2036 (15.26 million), reaching 16.66 million in 2040. In short, the elderly population will more than double over the next 20 years. The elderly share of the total population will rise from 16.1% this year to 20.7% in 2025, making Korea a super-aged society. That share will continue to rise rapidly, reaching 34.3% in 2040.
The domestic dependency ratio, defined as the number of children and elderly as a percentage of the working-age population, is expected to more than double over the next two decades, from 39.8% in 2020 to 79.7% in 2040.
By Lee Kyung-mi, staff reporter
Please direct comments or questions to [english@hani.co.kr]

Editorial・opinion
![[Column] Park Geun-hye déjà vu in Yoon Suk-yeol [Column] Park Geun-hye déjà vu in Yoon Suk-yeol](https://flexible.img.hani.co.kr/flexible/normal/500/300/imgdb/original/2024/0424/651713945113788.jpg) [Column] Park Geun-hye déjà vu in Yoon Suk-yeol
[Column] Park Geun-hye déjà vu in Yoon Suk-yeol![[Editorial] New weight of N. Korea’s nuclear threats makes dialogue all the more urgent [Editorial] New weight of N. Korea’s nuclear threats makes dialogue all the more urgent](https://flexible.img.hani.co.kr/flexible/normal/500/300/imgdb/original/2024/0424/7317139454662664.jpg) [Editorial] New weight of N. Korea’s nuclear threats makes dialogue all the more urgent
[Editorial] New weight of N. Korea’s nuclear threats makes dialogue all the more urgent- [Guest essay] The real reason Korea’s new right wants to dub Rhee a founding father
- [Column] ‘Choson’: Is it time we start referring to N. Korea in its own terms?
- [Editorial] Japan’s rewriting of history with Korea has gone too far
- [Column] The president’s questionable capacity for dialogue
- [Column] Are chaebol firms just pizza pies for families to divvy up as they please?
- [Column] Has Korea, too, crossed the Rubicon on China?
- [Correspondent’s column] In Japan’s alliance with US, echoes of its past alliances with UK
- [Editorial] Does Yoon think the Korean public is wrong?
Most viewed articles
- 1‘We must say no’: Seoul defense chief on Korean, USFK involvement in hypothetical Taiwan crisis
- 2N. Korean delegation’s trip to Iran shows how Pyongyang is leveraging ties with Moscow
- 346% of cases of violence against women in Korea perpetrated by intimate partner, study finds
- 4[Column] Park Geun-hye déjà vu in Yoon Suk-yeol
- 5‘Weddingflation’ breaks the bank for Korean couples-to-be
- 6Will NewJeans end up collateral damage in internal feud at K-pop juggernaut Hybe?
- 7Amnesty notes ‘erosion’ of freedom of expression in Korea in annual human rights report
- 8[Interview] Dear Korean men, It’s OK to admit you’re not always strong
- 9Korean government’s compromise plan for medical reform swiftly rejected by doctors
- 10[Editorial] Japan’s rewriting of history with Korea has gone too far