hankyoreh
Links to other country sites 다른 나라 사이트 링크
South Korea posts first ever automobile trade deficit with China

Between January and May of this year, South Korea posted its first deficit in automobile trade with China.
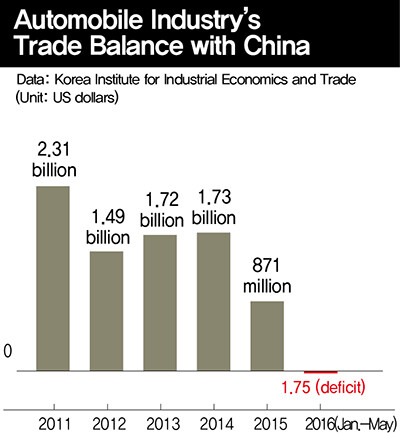
According to a report titled “The Switch to a Deficit in the Automobile Industry’s Trade Balance with China and Its Implications,” which was published by the Korea Institute for Industrial Economics and Trade (KIET) on July 21, South Korea posted a deficit of US$1.75 million in its automobile trade with China between January and May of 2016.
This is the first time that South Korea has had a deficit in trade with China in the automobile sector since trade between the two countries began in earnest with the establishment of diplomatic relations in 1992. The surplus in the automobile trade with China increased to US$2.3 billion in 2011 before dropping to US$871 million in 2015 and becoming a deficit in the first five months of this year.
The KIET’s report on South Korean automakers’ trade balance with China points to the perilous position of the domestic automobile industry. The first trade deficit with China in vehicle commerce speaks volumes about the rapid rise of Chinese companies, as well as China’s increasing tendency to reduce imports and Hyundai and Kia’s expanded production inside China.
Last year, 25 million automobiles were sold in China, which makes it by far the world’s largest automobile market. It is a critical market for Hyundai and Kia, since it accounts for more than 20% of all their overseas sales.
A combination of factors is responsible for the sharp decline in South Korean automobile exports to China, including South Korean automakers increasing production inside China and the growing competitiveness of Chinese companies.
After Hyundai and Kia acquired the capacity to produce 2.1 million vehicles a year inside China, their exports to China have decreased rapidly. These companies have for the most part produced their leading models - compact cars and sports utility vehicles – in China while exporting to China the models they do not produce there, including full-size cars and multi-purpose vehicles.
Exports from foreign companies operating in South Korea are also on the decline, as the parent companies increase their on-site production. Since last year, GM Korea has discontinued its finished car exports entirely and has only exported the parts for complete knock-down (CKD) cars.
Renault Samsung Motors, which is based in South Korea, had accounted for 35% of Renault’s exports to China, but with Dongfeng Renault (a joint venture between Renault and China’s Dongfeng Motor Company) opening up a factory in China in the first half of this year, Renault Samsung’s role is expected to gradually be reduced.
Another cause of the reduction in imports is sluggish sales resulting from China’s slowing economic growth. China’s automobile imports between January and May of this year were down 10.9% from the same period in the previous year.
The increasing competitiveness of Chinese companies – based on the domestic economy – is another noteworthy factor. Backed by large-scale facility expansion, favorable government policies and research and development, Chinese automakers have increased their share of the domestic market from 38% in 2014 to 41% in 2015.
“Chinese companies have adopted the strategy of developing a product line that is suited for the domestic market, improving their competitiveness and shedding their image of being cheap,” said Kim Gyeong-yu, an analyst with KIET. “They are expanding their market share based on sports utility models whose prices have stayed around 50% or 60% of those made by joint ventures while achieving a similar level of quality.”
The disparity in vehicle defects between local Chinese firm and joint ventures has continued to narrow since 2008. In addition, the percentage of local Chinese companies that have received five stars – the highest possible rating - in their safety assessments has increased from just 8.23% in 2006 to 92.5% in 2014.
In terms of volume, South Korean carmakers’ share of sales in the Chinese market has not fallen very much compared to the reduction in their exports there. Hyundai and Kia‘s exports to China represent less than 10% of their total sales. The two companies have four factories in China, and the vehicles they produce in China make up more than 90% of their total sales.
The problem is that while Hyundai and Kia have steadily increased their local production, their sales inside China are falling. The two South Korean firms are holding on to their position as the third most popular brand in China – after Volkswagen and GM – but there is no telling when they might take a tumble given the intensifying competition and the increasing pressure from Chinese carmakers.
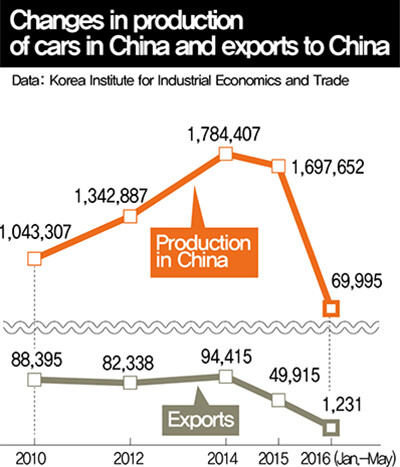
Hyundai and Kia have been growing quickly in China, topping one million vehicles produced in 2010 and manufacturing 1.7 million vehicles in the country last year. But those production figures were down 4.9% year on year, while their share in the Chinese market also slipped from 10% to 9%.
The fact that export volume is falling even as Kia and Hyundai are heavily dependent on production inside China is more troubling to South Koreans in relation to issues such as domestic employment. According to figures provided by Korea Auto Industries Cooperative Association, the number of automobiles produced in South Korea last year was 4,555,957, which was down 2.2% from 2011. During the same period, domestic production increased in China (33.0%), the US (39.9%) and Japan (10.5%).
By Hong Dae-seon, staff reporter
Please direct questions or comments to [english@hani.co.kr]

Editorial・opinion
![[Guest essay] Maybe Korea’s rapid population decline is an opportunity, not a crisis [Guest essay] Maybe Korea’s rapid population decline is an opportunity, not a crisis](https://flexible.img.hani.co.kr/flexible/normal/500/300/imgdb/original/2024/0430/9417144634983596.jpg) [Guest essay] Maybe Korea’s rapid population decline is an opportunity, not a crisis
[Guest essay] Maybe Korea’s rapid population decline is an opportunity, not a crisis![[Column] Can Yoon steer diplomacy with Russia, China back on track? [Column] Can Yoon steer diplomacy with Russia, China back on track?](https://flexible.img.hani.co.kr/flexible/normal/500/300/imgdb/original/2024/0430/1617144616798244.jpg) [Column] Can Yoon steer diplomacy with Russia, China back on track?
[Column] Can Yoon steer diplomacy with Russia, China back on track?- [Column] Season 2 of special prosecutor probe may be coming to Korea soon
- [Column] Park Geun-hye déjà vu in Yoon Suk-yeol
- [Editorial] New weight of N. Korea’s nuclear threats makes dialogue all the more urgent
- [Guest essay] The real reason Korea’s new right wants to dub Rhee a founding father
- [Column] ‘Choson’: Is it time we start referring to N. Korea in its own terms?
- [Editorial] Japan’s rewriting of history with Korea has gone too far
- [Column] The president’s questionable capacity for dialogue
- [Column] Are chaebol firms just pizza pies for families to divvy up as they please?
Most viewed articles
- 1First meeting between Yoon, Lee in 2 years ends without compromise or agreement
- 2Under conservative chief, Korea’s TRC brands teenage wartime massacre victims as traitors
- 3Months and months of overdue wages are pushing migrant workers in Korea into debt
- 4[Guest essay] Maybe Korea’s rapid population decline is an opportunity, not a crisis
- 5[Column] Can Yoon steer diplomacy with Russia, China back on track?
- 6‘We must say no’: Seoul defense chief on Korean, USFK involvement in hypothetical Taiwan crisis
- 7Dermatology, plastic surgery drove record medical tourism to Korea in 2023
- 8After election rout, Yoon’s left with 3 choices for dealing with the opposition
- 9Two factors that’ll decide if Korea’s economy keeps on its upward trend
- 10[Column] Behind factional animus of Korean politics, victim mentality festers